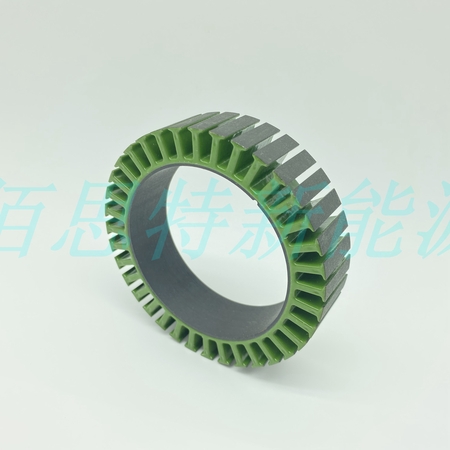
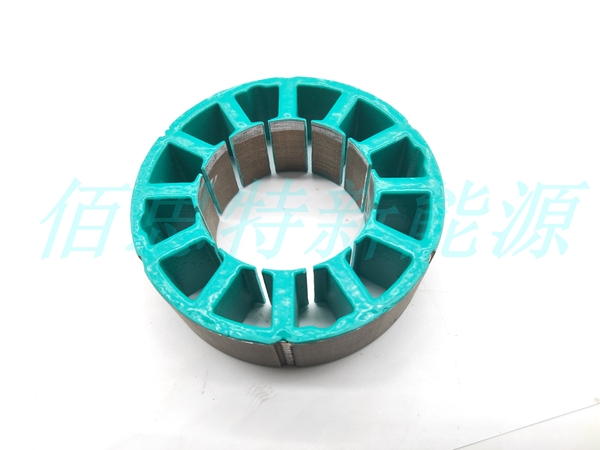
Stator Core Insulation Coating: Advantages, Methods, and Production Process
Choosing the wrong stator slot insulation can cause serious issues, from reducing winding efficiency to motor failure during high-voltage testing. Without the right insulation coating, your motor may not withstand harsh environments or high temperatures, leading to expensive repairs and downtime.
At best, we provide advanced stator insulation coating solutions that ensure maximum voltage protection, high temperature resistance, and reliable motor performance, helping you reduce costs and improve motor reliability.
Why Stator Slot Insulation Matters
Slot insulation is a critical factor in motor design. Choosing the wrong insulation can:
-
Reduce the slot fill factor of the winding
-
Cause insulation breakdown during high-voltage testing
-
Increase overall winding costs
Proper insulation ensures reliable motor performance, safety, and efficiency.
Common Insulation Methods for Stators
Motor designers generally use one of the following methods:
-
Injection molding
-
Slot paper
-
Stator insulation coating
Among them, stator insulation coating offers several advantages over injection molding and slot paper:
Advantages of Stator Coating
-
Adjustable Thickness – Thickness can be controlled to meet different voltage-withstand requirements, saving winding space and improving the slot fill factor.
-
High Temperature and Voltage Resistance – Can reach H grade, withstanding up to 180°C and a maximum voltage of 4000V.
-
High Production Efficiency – Using an electrostatic coating machine, daily output can reach 20,000 units.
-
Strong Adhesion – Improves the structural strength of the iron core.
-
Customizable Color – Optional colors for aesthetic or functional purposes.
Types of Insulation Coating
Electrostatic Coating
-
Thinner and more uniform coating thickness
-
Higher production efficiency (20,000 stators/day with automatic machine)
-
Mainly suitable for outer-rotor motors
-
Single-pass thickness rarely exceeds 0.5mm; thicker coatings require multiple passes
Thermoelectric Coating
-
Can coat inner-rotor, outer-rotor, coreless, special-shaped motors, and copper bars
-
Can handle complex shapes and large stators
-
Lower production efficiency (manual operation, dozens of stators/day)
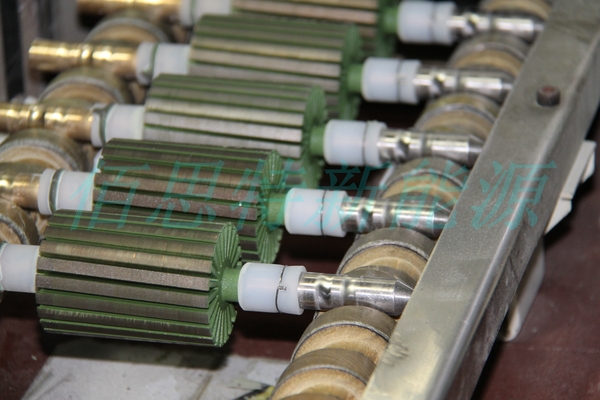
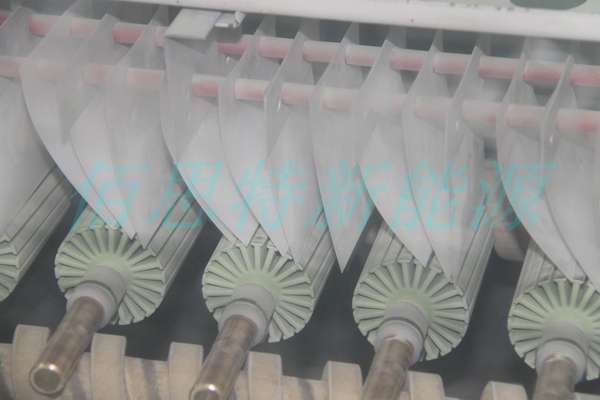
Stator Core Coating Production Process
The typical steps for applying iron core insulation coating include:
-
Ultrasonic cleaning
-
Baking to remove stamping oil, lubricating oil, and anti-rust oil
-
Fixture installation
-
Spraying
-
Fixture disassembly
-
Baking and curing
-
Voltage-withstand test and thickness detection
This process ensures consistent coating quality, high adhesion, and reliable insulation performance.


Contact Us
Looking for a reliable stator core insulation coating supplier?
We provide high-quality stator cores with electrostatic or thermoelectric coatings, customized to your voltage, temperature, and production requirements. Contact us today for samples or a quote.